The cold war is a period of geopolitical tension between the two world powers United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies. They are the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. It began following World War II. Historians do not fully agree on its starting and ending points. However, the period is generally considered from 1947 Truman Doctrine to the 1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union. The US led the Western Bloc. It included other First World countries. The USSR and its Communist Party dominated the Eastern Bloc.
Anti-communist and right-wing governments were supported by the US government. However, left-wing parties and revolutions were supported by the Soviet government. We are going to discuss the important events that led to the cold war.
Events that Led to the Cold War Timeline
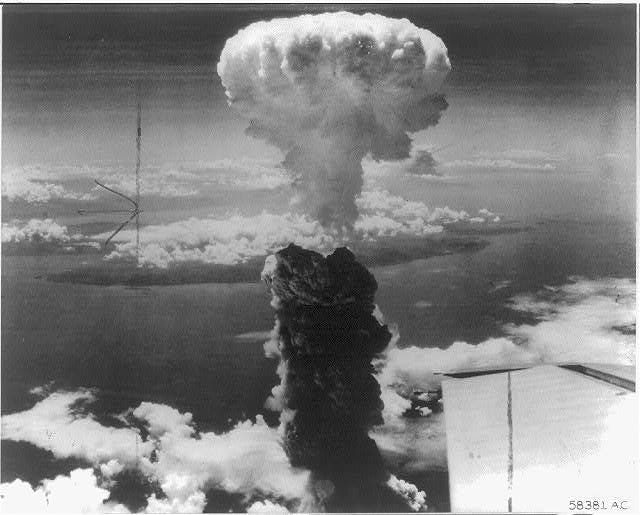
Hiroshima and Nagasaki Bombing (1945)
On August 6 and 9, 1945, the US dropped two atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. It was an attempt to end the Pacific War without a costly invasion of Japan. Little Boy was dropped on Hiroshima. Even after that, when Emperor Hirohito refused to heed President Truman’s call for surrender, another bomb named Fat Man was dropped on Nagasaki.

The US declared war on Japan. The two atomic bombings made Japan to surrender to the Allies. It effectively ended World War II. The use of atomic weapons showed America’s technological dominance, but it also increased tensions with USSR. Therefore, it is one of the key events that led to the cold war.
Communism Taking over Europe after WWII (1945)
The end of World War II brought about many changes in Europe. It completely destroyed many states. These states were in need of aid. Therefore, it led to the dependency of Europe on two non-European powers. America for Western Europe and USSR for Eastern Europe. Stalin used his influence to set up Communist governments in Eastern Europe. There actually exist here two different ideas. Firstly, of protection and hence the idea of buffer states. Secondly, the idea of the spread of Communism and hence satellite states. Stalin used these European countries to set up puppet-like regimes. After that, he could use their resources for the benefit of the USSR.

The ideology of Communism was that there could be no conflict of interest between the Communist states and the USSR. Therefore, by the late 1940s, pro-Soviet communist parties took power in Poland, Hungary, Romania, Albania, Bulgaria and so on.
Iron Curtain
Winston Churchill first used the term “Iron Curtain,” in his speech delivered on March 5, 1946. It is the line that split Europe into two separate political zones during the cold war. After World War II, the USSR created the iron curtain. Therefore, it was the political as well as ideological barrier between the two zones. While the Iron Curtain was in place, the countries of Eastern Europe and many in Central Europe were under the political influence of USSR. However, the states developed their own international economic and military alliances. These were the COMECON and the Warsaw Pact.

To the west of the Iron Curtain, the countries of Western and Southern Europe operated market economies. The democratic governments used to run these countries. However, most states to the west of the Iron Curtain were allies with the US within NATO. Economically, however, the European Community and the European Free Trade Association were the Western counterparts to COMECON.
Read Also:Ancient philosophers — everything you need to know about this
The Iron Curtain took physical form in the shape of border defences between the countries of the western and eastern blocs. They were the so-called inner German border between East and West Germany. The inner German border had markings in rural areas by double fences made of steel mesh with sharp edges. Near urban areas it was a high concrete barrier.
Truman Doctrine (1947)
The Truman Doctrine was a diplomatic policy of US. The strategy behind was to prevent Soviet geopolitical development during the Cold War. President Harry S. Truman introduced it to Congress on March 12, 1947. Therefore, it implied US support for any nation under the threat of Soviet communism. The Truman Doctrine became the foundation of American foreign policy. Therefore, it led to the formation of NATO in 1949.

The policy stated that US would provide political, military, and economic help to nations facing threats from external or internal democratic forces. As a result, the British Government announced that, it would no longer provide military and economic assistance to the Greek Government in its civil war against the Greek Communist Party. Truman asked Congress to support the Greek Government against the Communists.
Truman argued that the US owed it to “free peoples” to assist them in their fight against diplomatic states. According to him, It became the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are facing threats from armed minorities or outside pressures. According to historians, it was the among the events that led to the cold war.
Events that Led to the Cold War Intensification
Berlin Blockade and Airlift. (1948-1949)
The Berlin Blockade was one of the major events that led to the Cold War intensification. During post-World War II, the USSR blocked the Western Allies’ railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control. It was an attempt by the USSR to force the Western Allied powers to abandon their post-World War II authority in West Berlin.
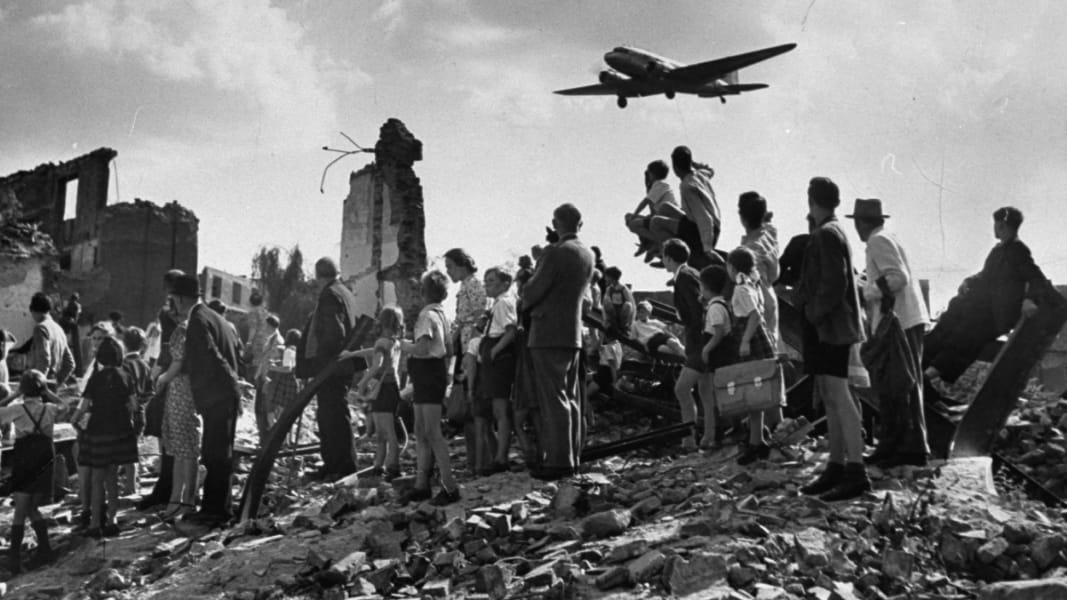

The Berlin Blockade was the first real test for the American policy of containment. Forcing their way into the city by land could have led to another war. Therefore, the Allies decided to supply their sectors of Berlin by air. This event became known as the Berlin Airlift. It lasted for eleven months. until the USSR lifted the Blockade in May 1949.
At the height of the Berlin Airlift, a plane landed in Berlin. It kept West Berlin supplied. However, this way cost the USA $350 million and Britain £17 million. Stalin was powerless to stop the Berlin Airlift. To shoot down the planes could have provoked World War Three. However, at that stage, the USSR did not have nuclear weapons.
Arms Race Between United States and Russia, USSR Tests First Nuclear Weapon (1949)
After the Berlin blockade and airlift, the USSR conducted its first nuclear test. The code-name was ‘RDS-1’. The device had a yield of 22 kilotons. On 29 August 1949, the USSR exploded its first atomic bomb. The fallout from the nuclear test drifted to the northeast, reaching the region of Altai Krai. However, the incident stamped the fact that US’s monopoly on nuclear weapons had been broken, U.S. President Truman publicly confirmed the news on 23 September 1949, and a day later by USSR itself. This was one of the key events that led to the cold war intensification.

Within a few years, the Cold War nuclear arms race between US and Russia was at full steam. However, in 1951, the United States exploded the first thermonuclear weapon. Two more years later, the USSR launched the RDS-6 test. Until the end of the Cold War, the United States would conduct 1,032 nuclear tests. The Soviet Union conducted 715. It caused high cancer rates, genetic defects and deformations in babies.
US Tests First Hydrogen Bomb (1950)
Also called a fusion bomb, hydrogen bomb, or H-bomb, a thermonuclear weapon is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Their destructive power is so great that they are among the most dangerous weapons humankind ever made. It even poses a threat to humanity as a whole. However, Truman announced his plan to build hydrogen bombs on Jan 31, 1950. He said, “It is part of my responsibility as commander in chief of the Armed Forces to see to it that our country is able to defend itself against any possible aggressor,”.

On November 1, 1952 the US tested a hydrogen device in the Pacific that vaporized an entire island, leaving behind a crater more than a mile wide. The test, code-named “Mike” was the first successful experiment of the concept for a superbomb. The explosion of this device had a yield that was 500 times larger than the atomic bomb dropped on Nagasaki.
Korean War (1950-1953)
On June 27, 1950, the United States officially entered the Korean War. The U.S. supported South Korea, to prevent an invasion from North Korea. The Korean War was a conflict that emerged after World War II. The Empire of Japan had occupied the Korean Peninsula during the war. After Japan’s defeat, the victorious Allies split the peninsula on the 38th parallel. U.S. troops occupied the southern part, while USSR troops occupied the northern part.
The two Koreas engaged in a border conflict, which escalated when North Korea invaded South Korea on June 25. However, the Korean War was a proxy war for the Cold War. The West—the United Kingdom and the U.S., supported South Korea. China and the USSR supported North Korea. The Korean War ended three years later, with millions of casualties. Therefore, the war ended with virtually no change in the border. The Korean Peninsula is still divided. The military personnel from both North and South Korea occupy the demilitarized zone (DMZ).
The Space Exploration (1957)
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War adversaries, the USSR and the US, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the missile-based nuclear arms race between the two nations following World War II. The USSR launched the world’s first artificial satellite in 1957, Sputnik 1. It marked the start of the space race. This was one of the key events that led to the cold war intensification.
After US president John F. Kennedy set a goal of “landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth”. Therefore, both countries started working on developing super heavy-lift launch vehicles. The US successfully deployed the Saturn V. It was large enough to send a three-person orbiter and two-person lander to the Moon. However, the US achieved its moon landing goal on July 1969, with the flight of Apollo 11 by sending humans. It was a single achievement o the Americans overshadowing all the other Soviet achievements.
Vietnam War (1955-1975)
The Vietnam War was a “proxy” war in the Cold War. Although the Soviet Union and the United States did not directly go to war. However, they each supported a different side in the war. It was a war between communist North Vietnam and the government of Southern Vietnam. Communist countries such as China and the USSR supported the North. Anti-communist countries, primarily the US supported the South. The war lasted from 1 November 1955 to 30 April 1975. It lasted for twenty years. The US lost the war and the country of Vietnam to the communists.
Events Led to the Cold War End
Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989)
Fall of the Berlin war was one of the key events that led to the cold war end. The Berlin Wall was a guarded concrete barrier. However, it was also a physical and ideological barrier that surrounded and separated West Berlin from East Berlin. The wall fell partly due to a bureaucratic error, but it did so amid a wave of revolutions that left the Soviet-led communist bloc on the verge of collapse and helped define a new world order.
The Reunification of Germany (1990)
Another major event that led to the cold war end was the reunification of Germany. It was the process in 1990 in which the German Democratic Republic became part of the Federal Republic of Germany to form the reunited nation of Germany. The iron curtain was lifted and Germany became reunited.
Dissolution of the Soviet Union (1991)
The Dissolution of the Soviet Union on December 25, 1991, was the event that marked the Cold War end. The disintegration of the USSR began in the late 1980s, with increasing instability in the various former Soviet states. It ended on December 26, 1991, when the Supreme Soviet voted to dissolve. 15 independent countries replaced the former superpower.
F.A.Q s
-
Who were the main countries involved in the Cold War?
Ans. The two world powers US and the Soviet Union. With their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc were involved in the Cold War.
-
Which events are included in the Cold War?
Ans. Containment of Russia, Arms Race Between the US & Russia, Development of the Hydrogen Bomb, Space exploration, and the fall of the Berlin Wall are major events included in the cold war.
-
Who was responsible for the Cold War?
Ans. The US and the USSR both contributed to the rise of the Cold War.
-
Why was it called the cold war?
Ans. The cold war was a long-lasting and continuous conflict between the US and USSR. It lasted from 1945 to 1989. It was called the Cold War because neither the USSR nor the United States officially declared war on each other.
-
What were the most important events and trends of the Cold War?
Ans.. The Berlin Blockade and Airlift, the Communist coups, the Greek civil war, the Korean War, the East Berlin uprising, etc.





